 |
| HDD & SSD |
HDD -- Hard Disk Drive
SSD -- Solid State Drive
Solid state drives and hard disk drives are similar in their physical specifications, but they store data very differently. There are advantages and disadvantages to each type of drive, and deciding on which type is right for you comes down to what you use your computer for. Hope this post shows you how each type of storage drive works and what it means for you.
HDD: Hard Disk Drive:
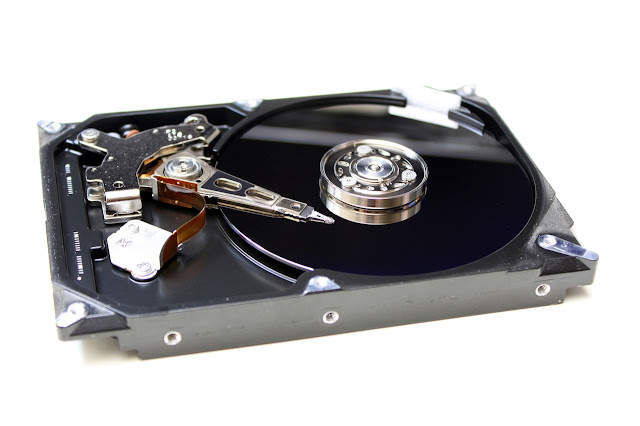
This technology behind HDD is well-known and well-tested and it's for more than 5-6 decades, steadily increasing their storage capacity and decreasing their physical size. HDDs rely on spinning disks or platters to read and write data.
 |
| HDD |
How Hard Drives works:
Hard disk drives consist of one or more magnetically sensitive platters, an actuator arm with a read/write head on it for each platter, and a motor to spin the platters and move the arms. There is also an I/O controller and firmware that tells the hardware what to do and communicates with the rest of the system. Each platter is organized into concentric circles, called tracks. Tracks are divided into logical units called sectors. Each track and sector number results in a unique address that can be used to organize and locate data. Data is written to the nearest available area. There is an algorithm that processes the data before it’s written, allowing the firmware to detect and correct errors. The platters spin at preset speeds (4200 rpm to 7200 rpm for consumer computers), those speeds correlate to read/write rates. The higher the preset speed, the faster a hard drive will be able to read and write data.
Each time you ask your computer to retrieve or update data, the I/O controller tells the actuator arm where that data is located, and the read/write head gathers the data by reading the presence or absence of a charge in each address. If the request was to update the data, the read/write head changes the charge on the affected track and sector.The time it takes for the platter to spin and the actuator arm to find the correct track and sector is known as latency.
Drawbacks:
Benefits:
Drawbacks:
The benefits:
Conclusion:
The drawbacks to HDDs are a result of the mechanical parts used to read and write data, as physically finding and retrieving data takes more time than electronically finding and retrieving data. The mechanical parts can skip or even fail if they are handled roughly or dropped. This is a concern in laptops, but not as much in desktops. HDDs are also heavier and use more energy than comparable SSDs.
Benefits:
The benefits of a hard disk drive are that they are a proven technology, are frequently less expensive than a solid state drive for the same amount of storage. Currently, HDDs are also available with more storage space than SSDs.
SSD: Solid State Drive:
This is a new technology, but have progressed drastically / rapidly, adding more storage capacity each year. SSDs rely on eletronic storage in non-volatile memory, meaning data won't disappear when the computer is turned off.
 |
| SSD |
How Solid State Drive Works:
We can consider SSDs as a large USB drives, they use the same base technology, which is NAND. The technology used in SSDs are kind of flash memories. At the lowest level, floating gate transistors record a charge (or lack of a charge) to store data. The gates are organized in a grid pattern, which is further organized into a block. Block size can vary, but each row that makes up the grid is called a page. There is an SSD controller that performs several functions, including keeping track of where data is located.
Reading and writing:
Each time you ask your computer to retrieve or update data, the SSD controller looks at the address of the data requested and reads the charge status. Updating data is more complex for SSDs. All the data in a block must be refreshed when any portion of it is updated. The data on the old block is copied to a different block, the block is erased, and the data is rewritten with the changes to a new block. When the drive is idle, a process called garbage collection goes through and makes sure the information in the old block is erased and that the block is free to be written to again.
There is another process, called TRIM, that informs the SSD that it can skip rewriting certain data when it erases blocks. Because there are a finite number of times any block can be rewritten, this is an important process that prevents premature wear on the storage drive. To further prevent wear on the drive, there is an algorithm to make sure that each block in the drive gets an equal amount of read/write processes. This process is called wear leveling and happens automatically as the drive is working. Because the read/write process requires data movement, SSDs are usually overprovisioned with storage; there is always a certain amount of the drive that is not reported to the operating system, and not accessible to the user. This allows room for the drive to move and delete items without affecting the overall storage capacity.
Drawbacks:
SSDs are newer technology, and as such, are more expensive than HDDs. Although they are catching up, it can be harder to find very large-capacity solid state drives. HDDs can be as much as 2.5 times larger.
The benefits:
Solid state drives deliver faster load times for games, applications, and movies. Because of the technology they use, SSDs are lighter and more able to withstand being moved and dropped. In addition, solid state drives use less energy, keeping the computer they’re used in cooler.
Conclusion:
The difference between hard drives and solid state drives is in the technology used to store and retrieve data.
HDDs are cheaper and you can get more storage space. SSDs, however, are faster, lighter, more durable, and use less energy. Your needs will dictate which storage drive will work best for you. The table below illustrates some of the differences.
Cost
|
Speed
|
Durability
|
Highest
Capacity
|
Energy
Efficiency
|
|
HDD
|
Cheaper
|
Slower
|
Less
durable
|
10
TB
|
Use
more energy
|
SSD
|
More expensive
|
Faster
|
More durable
|
4 TB
|
Use less energy
|
Want to buy HDD or SSD please do click here.
I am looking to change my laptop's HDD to SSD. How to change my laptop's HDD to SSD?.I know the benefits of using SSD. But don't know how to do it. Would appreciate your help.
ReplyDeleteHi Ashhhh,
DeleteThat's a good move, i appreciate that.
There are different types of implementation, One of them is mentioned below
Please do follow these steps :
1. Take Data Backup from old / current HDD of your laptop.
Hope you checked for the slot available for SSD on your laptop and upgradation compatibility / support on your laptop. If it is so follow these simple steps.
2. Take your new SSD fix it on respective slot & put OS on-to it.
3. Copy the data on-to the SSD & Ta-da it's done.
Let me create a post on it.
On above method if you are facing any issues let us know.
By the way thanks for coming up with different questions.....
Hope this point would helped you in nice way..